What's in a SWMS?
SWMS overview
A Safe Work Method Statement typically has seven sections, which are:
- Job details
- Tasks, risks and controls
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Emergency procedures
- Communications
- Worker register
- Review and approver signing page
There is often also a risk matrix to explain how something gets classified low, medium or high risk.
It’s worth noting that these sections are not strictly required under regulation. The PCBU is required to identify and control risks where high risk construction exists. They also need to consultant and inform workers and relevant people. The sections of the SWMS are designed to support this requirement.

1. Job details
This section covers the basic details of the job including:
- PCBU – Person Conducting Business or Undertaking, i.e. who’s doing the work. They’re responsible for the SWMS.
- Activity – what sort of work is being done
- HRCW – what’s the relevant High Risk Construction Work
- Project – what’s the broader project, if there is one
- Works manager – who’s supervising the work on site
- Principal contractor – who’s managing the overall project, or is responsible for the work site
- SWMS reviewer – who from the principal contractor is signing off the SWMS
- Responsible for compliance – who’s making sure the SWMS is being followed in terms of controls and workers engaged in the work. This is usually someone from the PCBU.
2. Tasks, risks and controls
This section is what really matters. This is where you need to identify all risks related to the HRCW and develop control measures to reduce the risk.
- Tasks – list each task or jobs step in the work
- Hazards & risks– describe the related hazard or risk
- Risk rating – assign a risk rating without any control put in place
- Control measure – describe what controls you have or will put in place to lower the risk as much as possible
- Residual risk – what’s the level of risk after the control is in place
- Responsible person – the person who’s responsible for each task and control
3. Personal Protective Equipment
The PPE section is also very important and it HRCW often requires specific equipment for the work and for safety. Common types of PPE include:
- Hard hat – protection from falling objects and hitting hard immovable objects
- High vis vest– to make sure people are easily seen on a site, especially near heavy equipment
- Steel capped boots – protection from heavy objects being dropped
- Safety glasses – to stop sparks, dust and debris getting in eyes
- Gloves – protection from sharp and hot objects to stop cuts and burns
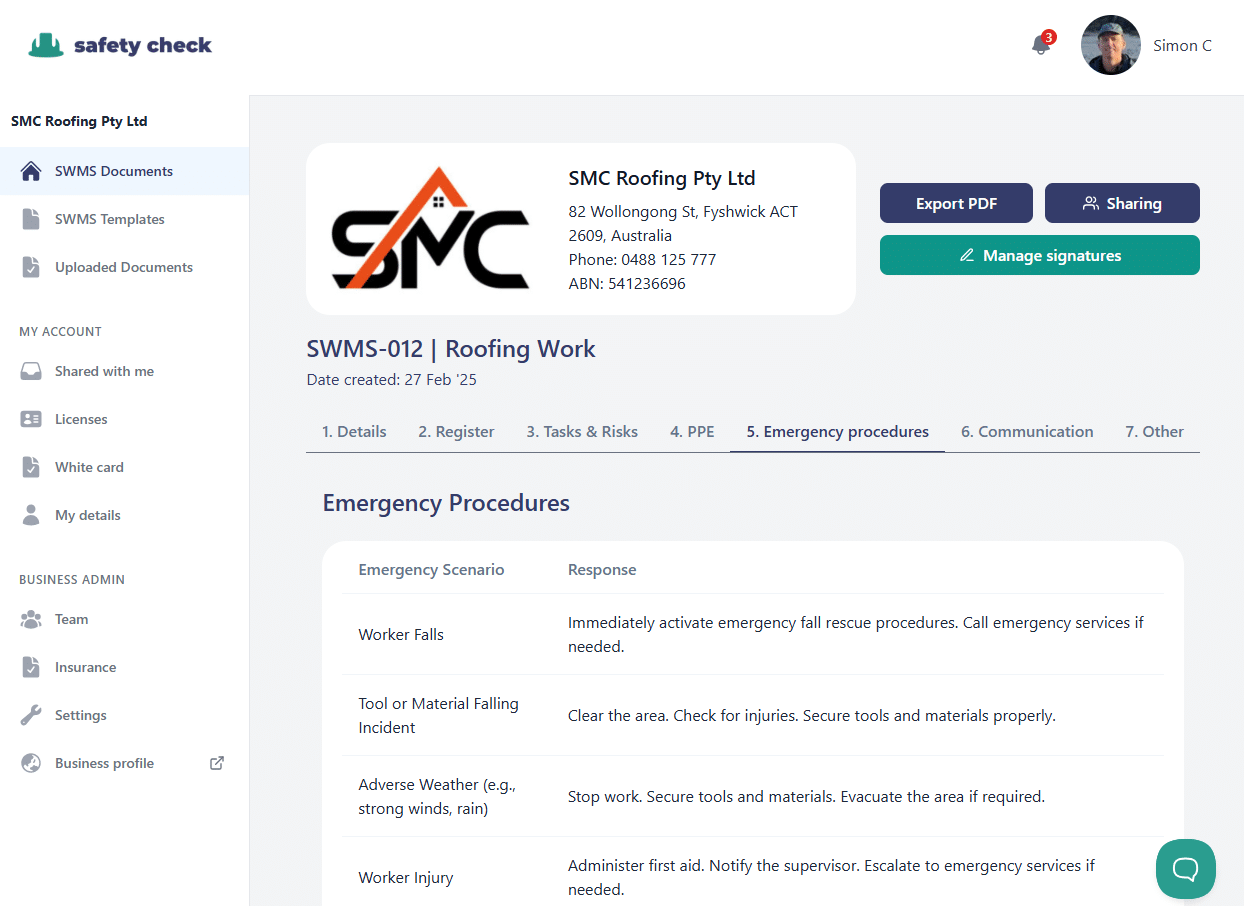
4. Emergency procedures
If something does go wrong during the job, it’s critical to have thought through emergency procedures. These cover incidents where there’s been a major or minor injury or if an incident has made working conditions unsafe and needs to be rectifies. Changes to work conditions can al so include adverse weather.
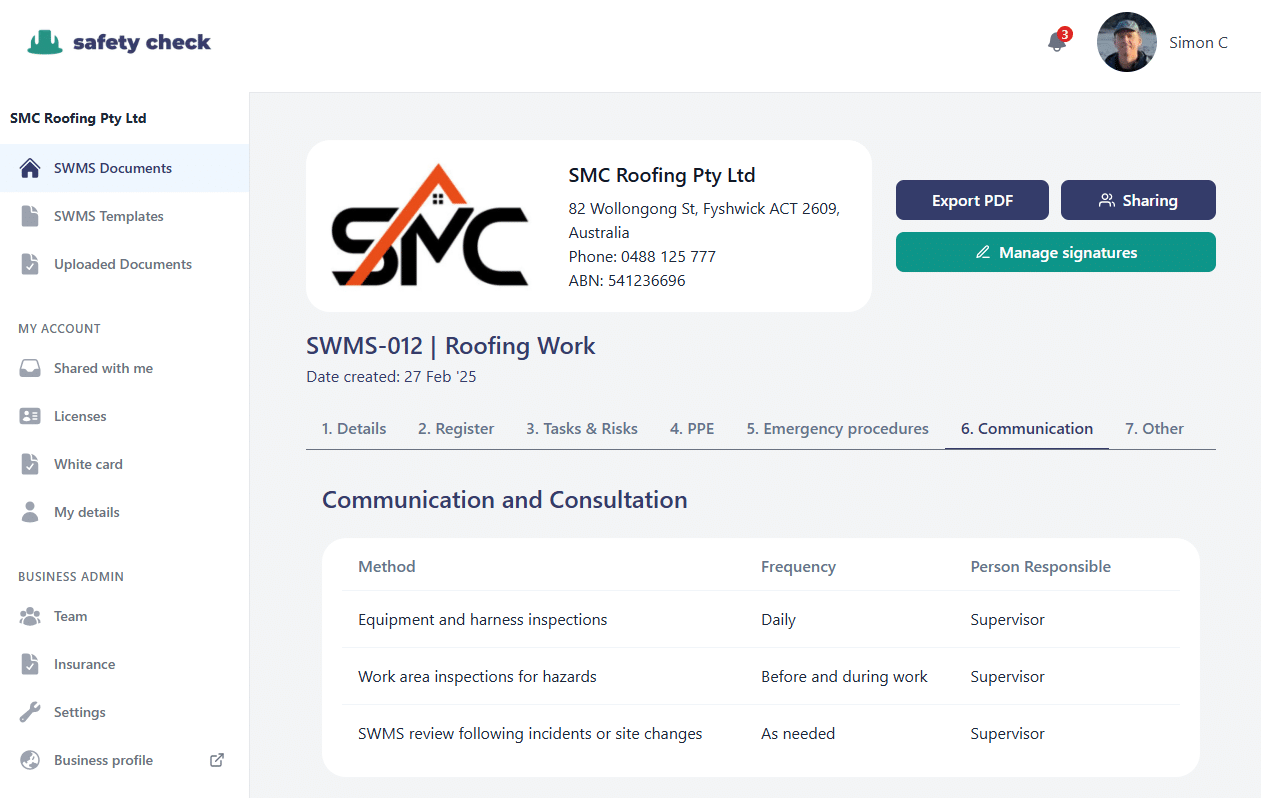
5. Communications and consultation
Regular communication is key to maintaining a safe construction work site. Useful meetings and procedures include:
- SWMS review – in particular when there is a major change on the work site, or an incident or on large and complex work sites
- Toolbox talk – these meetings are a good flexible general session for running any building site and can be added to a SWMS as a requirement
- Equipment inspections – faulty equipment can create hazards and some cases requires regular testing under a test and tag procedure
6. Worker register
All workers engaged in the HRCW should be consulted during the creation of the SWMS and acknowledge the document with a signature.
The register should have their name, role, signature and the date and time of signing.
SafetyCheck does this digitally, which works well on mobile without the need for an app or logging into an account.
7. Approval and signing page
Others who must sign the SWMS are the:
- PCBU,
- Person Responsible for Compliance (generally from the PCBU), and
- SWMS reviewer (from the Principal Contractor)
The Principal Contractor may also require signatures from various safety managers, engineers or other specialists.
SWMS made easy
Safe Work Method Statement templates and tools for small aussie trade businesses.